Your cart is currently empty!

How to Become a Cybersecurity Analyst in 2025: A Comprehensive Guide
The demand for cybersecurity analysts has skyrocketed as organizations increasingly prioritize securing their digital assets. If you’re passionate about protecting data and mitigating cyber threats, this career path could be ideal for you. This guide walks you through everything you need to know to become a cybersecurity analyst, drawing insights from expert sources and practical…
The demand for cybersecurity analysts has skyrocketed as organizations increasingly prioritize securing their digital assets. If you’re passionate about protecting data and mitigating cyber threats, this career path could be ideal for you. This guide walks you through everything you need to know to become a cybersecurity analyst, drawing insights from expert sources and practical examples.
Table of Contents
What Does a Cybersecurity Analyst Do?
Cybersecurity analysts are responsible for safeguarding an organization’s computer networks and systems from cyberattacks. Their roles typically involve:
- Monitoring networks for suspicious activity.
- Investigating breaches and vulnerabilities.
- Installing and managing firewalls and encryption programs.
- Conducting penetration testing to identify weaknesses.
- Educating staff about cybersecurity best practices.
Steps to Become a Cybersecurity Analyst
1. Understand the Role
Cybersecurity analysts play a pivotal role in safeguarding organizations from digital threats. This requires an understanding of common cyber threats, including:
- Malware: Malicious software designed to damage or disrupt systems.
- Phishing: Fraudulent attempts to steal sensitive information.
- Ransomware: Software that locks users out of their systems until a ransom is paid.
- DDoS Attacks: Overwhelming systems with traffic to cause disruptions.
2. Educational Background
Degree Requirements
While not always mandatory, obtaining a relevant degree can significantly boost your chances of entering the field. Recommended fields include:
- Computer Science
- Information Technology
- Cybersecurity
Certifications
Professional certifications demonstrate expertise and commitment. Here’s a comparison of popular certifications:
| Certification | Issued By | Benefits |
| CompTIA Security+ | CompTIA | Covers foundational cybersecurity concepts. |
| Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) | EC-Council | Focuses on penetration testing and hacking techniques. |
| Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) | (ISC)² | Suitable for experienced professionals managing security systems. |
| CompTIA Cybersecurity Analyst (CySA+) | CompTIA | Focuses on behavior analytics to prevent threats. |
3. Develop Technical Skills
Key Skills
To excel as a cybersecurity analyst, master the following:
- Networking: Understand protocols like TCP/IP, DNS, and VPNs.
- Operating Systems: Gain familiarity with Windows, Linux, and macOS environments.
- Programming: Learn languages such as Python and PowerShell for automation.
- Threat Analysis: Develop skills to analyze malware behavior and attack tactics.
4. Gain Practical Experience
Internships
Start with roles like IT support or junior administrator to understand foundational concepts.
Online Platforms
Use virtual labs to build hands-on experience:
- TryHackMe: Beginner-friendly cybersecurity challenges.
- Hack The Box: Advanced penetration testing exercises.
5. Learn Tools and Technologies
Cybersecurity analysts rely on a suite of tools to protect systems effectively:
| Tool | Functionality | Real-World Usage Example |
| Wireshark | Packet analysis for network troubleshooting. | Used to identify malicious traffic during a network attack. |
| Metasploit Framework | Penetration testing toolkit. | Simulating real-world attacks to find system vulnerabilities. |
| Nessus | Scans for vulnerabilities in systems. | Regular scans to ensure compliance with security standards. |
| Splunk | SIEM (Security Information and Event Management). | Analyzing logs to detect anomalies in real-time. |
| Burp Suite | Tests web application security. | Finding and fixing flaws in web applications before deployment. |
6. Build a Portfolio
A strong portfolio showcases your skills and projects. Include:
- Reports on security vulnerabilities you’ve mitigated.
- Projects from labs or simulations, such as creating firewalls or detecting threats.
- Real-world experiences from internships or volunteer work.
7. Networking and Continuous Learning
Professional Networking
Join communities and attend conferences like DEF CON or Black Hat to connect with experts.
Staying Updated
Given the rapid evolution of cyber threats, stay current by:
- Following blogs like Krebs on Security.
- Participating in online forums such as Reddit’s r/cybersecurity.
- Enrolling in continuous education courses from platforms like Cybrary or SANS Institute.
8. Seek Career Mentorship
Finding a mentor in the cybersecurity field can provide invaluable guidance and open opportunities. Many professionals in the U.S. offer mentorship through LinkedIn or professional organizations like ISACA and ISSA.
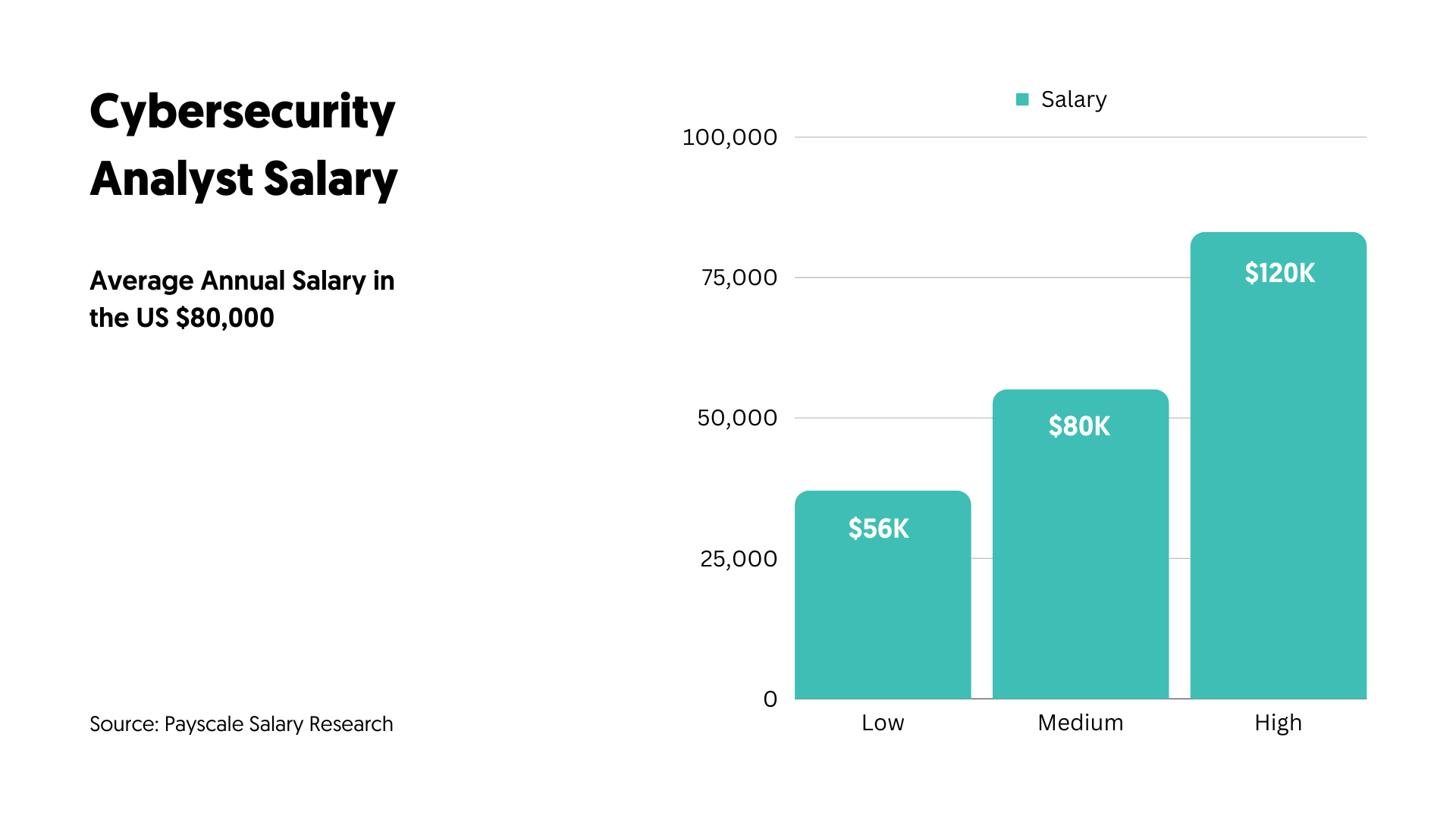
Career Path and Salary Outlook
Cybersecurity offers a promising career trajectory. Here’s what to expect:
| Job Title | Average Salary (USA) | Key Responsibilities |
| Junior Cybersecurity Analyst | $65,000 – $80,000 | Monitoring systems and reporting threats. |
| Cybersecurity Analyst | $85,000 – $110,000 | Investigating breaches and developing prevention strategies. |
| Senior Analyst | $115,000 – $140,000 | Leading teams and managing cybersecurity programs. |
| Cybersecurity Manager | $140,000+ | Overseeing an organization’s entire security framework. |
Common Challenges in Cybersecurity
- Evolving Threats: Cybersecurity analysts must constantly learn to counter new threats.
- Work Pressure: High responsibility in protecting sensitive data can lead to stress.
- Complex Problem-Solving: Requires critical thinking and analytical skills.
FAQs
Can You Become a Cybersecurity Analyst with No Experience?
It helps to have a degree in computer science or a software field to land a cybersecurity analyst job. That said, individuals who have completed courses in cybersecurity, or who have a significant number of projects under their belt, do have a shot at a cybersecurity job with no prior experience.
What Is the Difference Between a Cybersecurity Analyst and a Cybercrime Investigator?
Cybersecurity analysts keep a company’s IT and network systems safe without focusing on the legality of the actions of malicious actors. Cybercrime investigators conduct inquiries into illegal activities online.
Is It Hard To Become a Cybersecurity Analyst?
It’s not hard to pick up the skills required to be a cybersecurity analyst. There are various boot camp programs and professional certifications that you can take to quickly pick up skills in the area. The most important thing to do is find a mentor and constantly network among professionals in the field so that you’re aware of new positions when they open up.
Do You Need a Degree to Become a Cyber Analyst?
You don’t need a degree to become a cybersecurity analyst, though it can be helpful. Many professionals enter the field through certifications like CompTIA Security+ or CEH and hands-on experience. Practical skills, continuous learning, and relevant certifications are often more valuable than formal education in this dynamic field.
Final Thoughts
Becoming a cybersecurity analyst requires a combination of education, skills, and hands-on experience. With the growing importance of cybersecurity, professionals in this field enjoy excellent career prospects and the opportunity to make a significant impact in protecting data and systems.
Start your journey today by exploring certifications, gaining technical skills, and diving into the world of ethical hacking and threat mitigation.
Interesting Read: Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)-New Guidelines-2025 – Tech To Know


