Your cart is currently empty!

The Future of Automotive Technology: How Innovation is Driving the Cars of Tomorrow
I grew up in an era when nobody thought of cars without petrol or diesel. But this will become a myth in the upcoming days. The automotive industry has taken a seismic shift, and I find it fascinating to witness how rapid technological advancements are reshaping the way we think about cars. It’s no longer…
I grew up in an era when nobody thought of cars without petrol or diesel. But this will become a myth in the upcoming days. The automotive industry has taken a seismic shift, and I find it fascinating to witness how rapid technological advancements are reshaping the way we think about cars. It’s no longer just about getting from point A to point B, today’s innovations are transforming vehicles into powerful machines of sustainability, intelligence, and connectivity.
From electric vehicles (EVs) revolutionizing eco-friendly transportation to self-driving cars challenging the very idea of human drivers, the pace of change is truly mind-blowing. As I dive into this article, I want to take you along to explore the groundbreaking trends that are defining the future of automotive technology.
Together, we’ll unpack everything from key concepts and examples to comparisons that highlight just how far we’ve come and where we’re headed. Let’s discover how these innovations are shaping the cars of tomorrow and, ultimately, redefining the way we move.
Table of Contents
1. Electric Vehicles aka EVs: The Green Revolution
What Are EVs?
Electric vehicles (EVs) are revolutionizing the automotive industry by offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Unlike conventional cars that rely on gasoline or diesel, EVs are powered entirely or partially by electricity stored in rechargeable batteries. Fully electric vehicles (like the Tesla Model 3 or Nissan Leaf) run solely on battery power, while plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) combine a battery with a small gasoline engine for extended range.
One of the standouts features of EVs is their ability to produce zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing their carbon footprint and contributing to cleaner air in urban areas. This makes them a key player in the fight against climate change. Additionally, EVs are remarkably quiet, offering a smoother and more serene driving experience compared to the roar of a traditional engine.
Interesting Read: Top 10 Best Electric Cars to Watch in 2025 for a Greener Future
Key Advancements in EV Technology
Recent advancements in EV technology are helping to overcome challenges like limited range, long charging times, and high costs, making these vehicles more accessible and practical for everyday use.
Examples and Comparisons
The electric vehicle (EV) market is flourishing with a variety of models catering to different needs, from high-performance luxury sedans to rugged adventure pickups. Below are some standout EVs and their unique features:
Tesla Model S Plaid
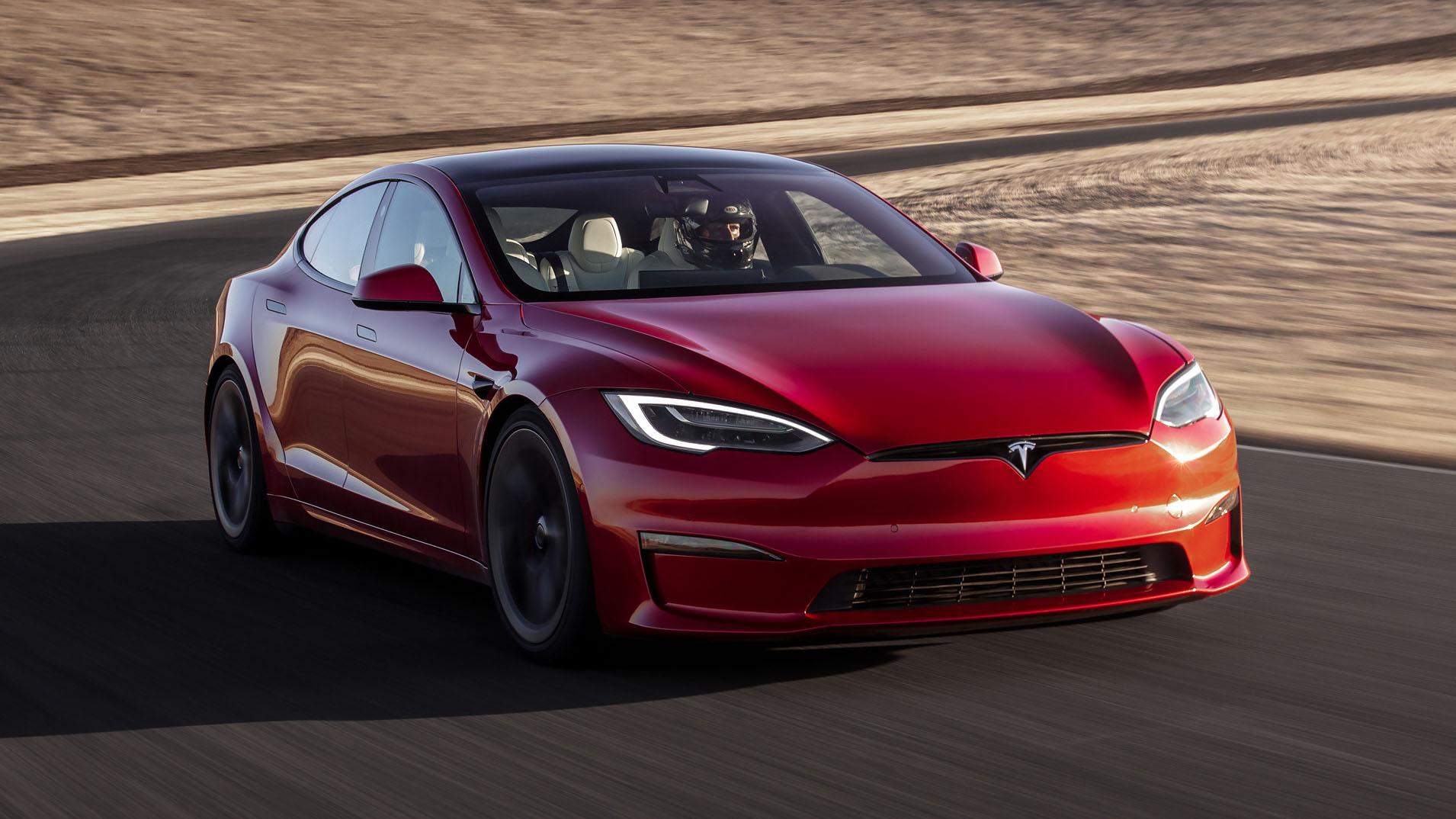

- Highlights: Renowned for its record-breaking acceleration, the Model S Plaid can go from 0 to 60 mph in a mind-boggling 1.99 seconds. With a long range of up to 396 miles, it’s a favorite for luxury and performance enthusiasts.
Rivian R1T
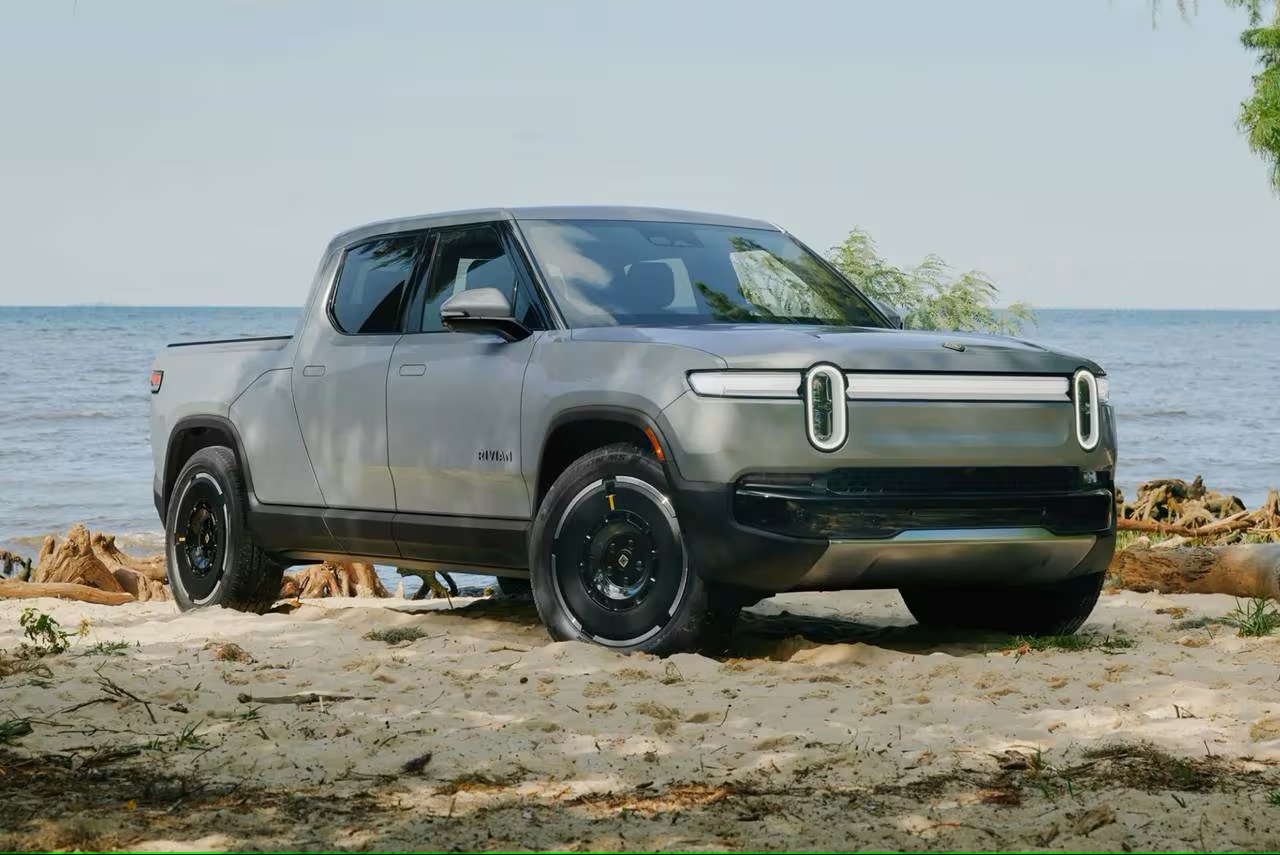

- Highlights: A trailblazing electric pickup truck designed for adventure. Its off-road capabilities, impressive towing capacity, and unique “gear tunnel” storage set it apart.
Ford F-150 Lightning
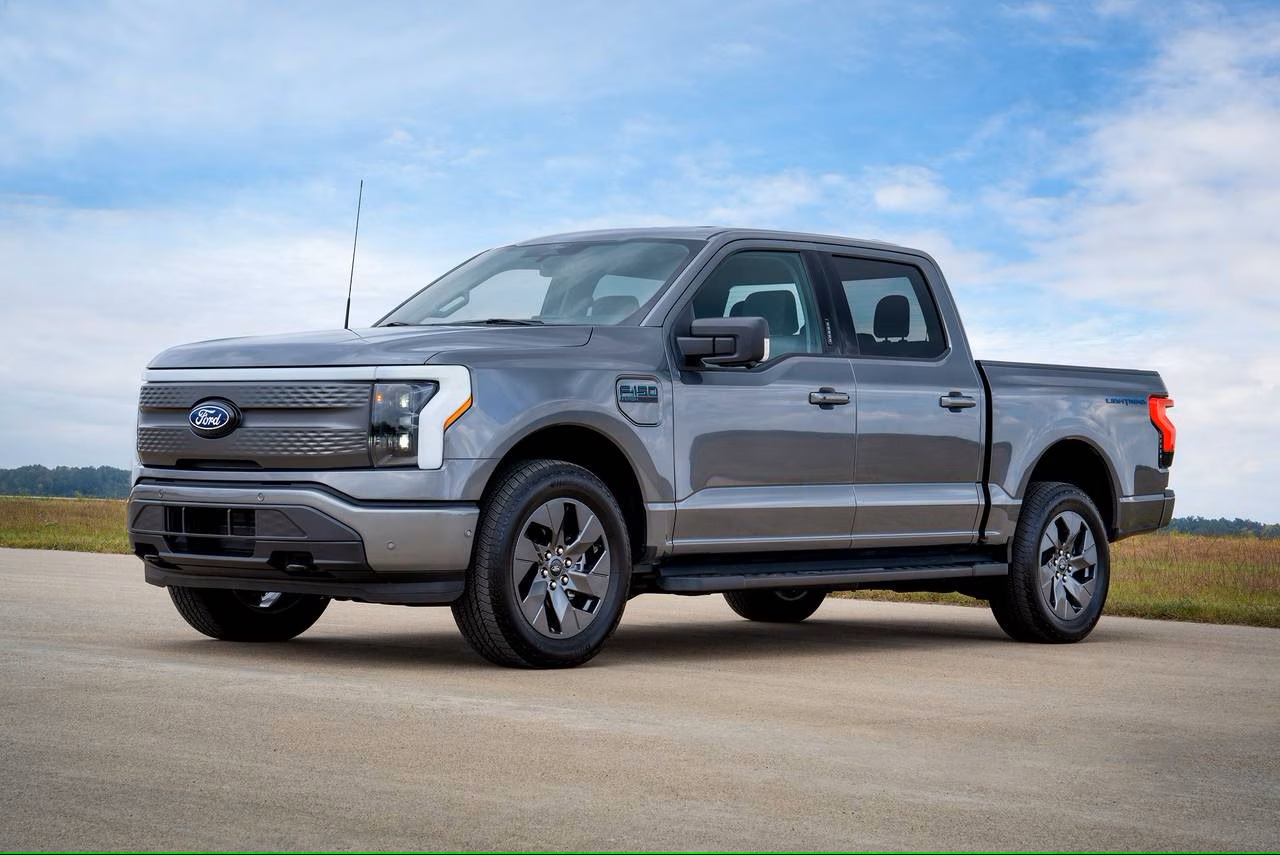

- Highlights: This electric version of the popular F-150 combines the practicality of a pickup with innovative features like a massive front trunk (frunk) and the ability to power your home during outages.
Lucid Air Dream Edition

- Highlights: A luxury sedan offering unparalleled range (up to 516 miles) and cutting-edge interior technology. It’s a strong contender in the high-end EV market.
Hyundai Ioniq 5

- Highlights: A stylish, compact crossover with retro-futuristic design. It offers rapid charging (10% to 80% in 18 minutes) and a comfortable interior, making it ideal for families.
Porsche Taycan

- Highlights: A high-performance sports EV known for its dynamic driving capabilities, luxurious interiors, and rapid charging speed.
Comparison Table
| Model | Acceleration (0-60 mph) | Range (miles) | Charging Speed (Fast Charger) | Key Features | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tesla Model S Plaid | 1.99 seconds | 396 | 200 miles in 15 minutes | Blistering performance, luxury | Performance and luxury enthusiasts |
| Rivian R1T | 3.0 seconds | 314 | 140 miles in 20 minutes | Off-road capabilities, gear tunnel | Adventure and outdoor enthusiasts |
| Ford F-150 Lightning | 4.0 seconds | 320 | 150 miles in 20 minutes | Power for home, practical features | Contractors and families |
| Lucid Air Dream Edition | 2.5 seconds | 516 | 300 miles in 20 minutes | Unmatched range, luxury interior | Long-range and luxury-focused drivers |
| Hyundai Ioniq 5 | 5.2 seconds | 303 | 10% to 80% in 18 minutes | Retro-futuristic design, practicality | Families and style-conscious buyers |
| Porsche Taycan | 2.6 seconds | 246 | 60 miles in 4 minutes | Sports car performance, luxury | Sports car and driving enthusiasts |
2. Autonomous Driving: The Road to Self-Driving Cars
Autonomous driving, often referred to as self-driving or driverless technology, is a groundbreaking advancement in automotive engineering that enables vehicles to navigate roads and perform driving tasks with minimal or no human input. These vehicles rely on a combination of sophisticated software, sensors, and artificial intelligence (AI) to make real-time decisions, ensuring safety and efficiency. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has classified autonomous driving into six levels, ranging from Level 0 (no automation, where the driver is fully in control) to Level 5 (full automation, where no human input is required).
Key Technologies Powering Autonomous Driving
- AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are at the core of autonomous driving systems. These technologies enable vehicles to:- Recognize objects: Identify pedestrians, other vehicles, road signs, and lane markings.Predict behavior: Anticipate the actions of nearby vehicles and pedestrians to avoid collisions.Make decisions: Choose the optimal route, adjust speed, or change lanes based on traffic conditions and real-time data.
- Sensors and Cameras
Autonomous vehicles use a suite of sensors to perceive their surroundings. These include:- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): Emits laser beams to create a 3D map of the vehicle’s environment, crucial for detecting obstacles and measuring distances.
- Radar: Measures the speed and distance of objects, especially useful for detecting other vehicles in poor visibility conditions.
- Cameras: Provide high-resolution visuals for identifying road signs, traffic signals, and lane markings.
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
Autonomous vehicles are increasingly integrating V2X communication technology to interact with other vehicles, infrastructure, and even pedestrians. This includes:- Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V): Sharing data like speed, location, and braking to prevent collisions.
- Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I): Communicating with traffic lights and road sensors to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
- High-Definition (HD) Mapping
Autonomous vehicles rely on detailed HD maps that include precise information about road layouts, elevation, and traffic patterns. These maps work in tandem with real-time sensor data to ensure accuracy in navigation. - Edge Computing and 5G Connectivity
Autonomous vehicles process vast amounts of data in real time. Edge computing allows this data to be analyzed closer to the source, reducing latency. Coupled with 5G connectivity, vehicles can receive updates and communicate with their environment almost instantaneously.
Levels of Autonomy (SAE Classification)
The table below outlines the six levels of vehicle autonomy as defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). It highlights the progression from no automation (Level 0) to full automation (Level 5), showcasing the key features and examples of each level.
| Level | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Level 0 | No automation; the driver is fully in control. | N/A |
| Level 1 | Driver assistance, such as adaptive cruise control or lane-keeping systems. | Basic cruise control, lane-keeping assist |
| Level 2 | Partial automation, where the car controls steering and acceleration but requires constant supervision. | Tesla Autopilot, GM Super Cruise |
| Level 3 | Conditional automation, where the vehicle drives itself under certain conditions but requires the driver to take over when prompted. | Audi A8 Traffic Jam Pilot |
| Level 4 | High automation, where the vehicle operates without human input in specific environments. | Waymo’s self-driving taxis, Cruise Origin |
| Level 5 | Full automation, where no human input is needed, and the car can handle any driving situation (still under development). | N/A (Future Tech) |
Examples and Comparisons
Tesla Autopilot

- A Level 2 autonomous driving system.
- Features: Adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping, automatic lane changes, and traffic-aware navigation.
- Focus: Consumer vehicles with incremental advancements toward full autonomy.
Waymo One

- A Level 4 autonomous ride-hailing service.
- Features: Fully driverless rides in designated areas, leveraging advanced LiDAR and mapping technology.
- Focus: Revolutionizing ride-sharing with fully autonomous vehicles in select cities like Phoenix, Arizona.
Mercedes-Benz Drive Pilot
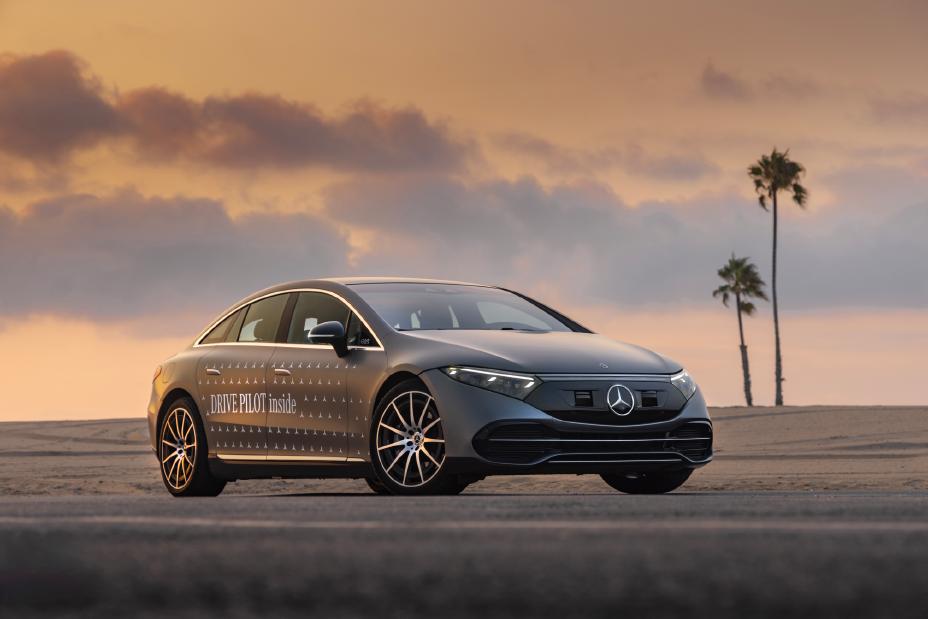

- A Level 3 autonomous driving system.
- Features: Hands-free driving in specific conditions on highways, with human intervention only when prompted.
- Focus: Luxury vehicles offering advanced automation for improved convenience and safety.
Cruise Origin (by General Motors)
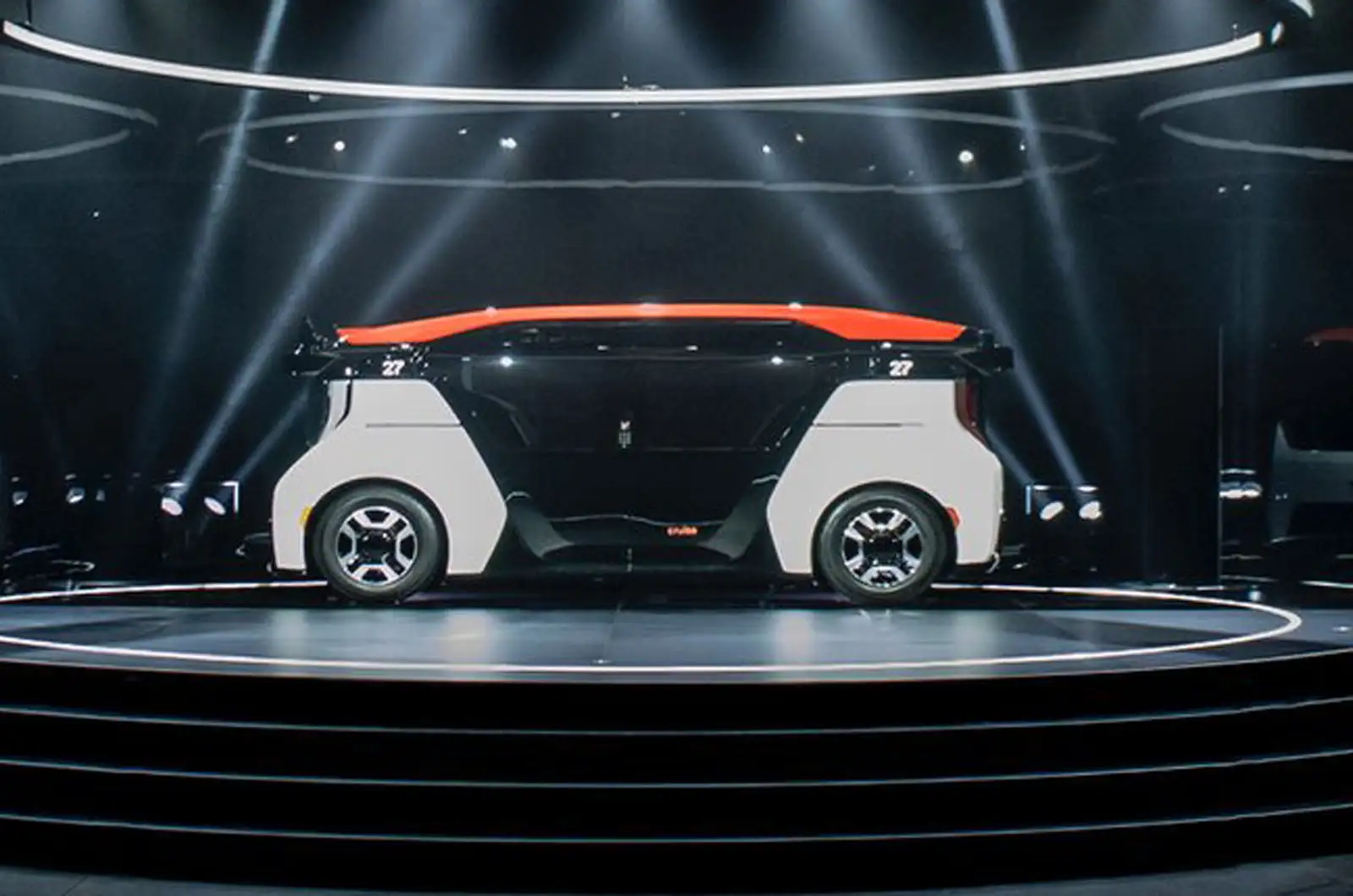

- A Level 4 autonomous shuttle.
- Features: Fully driverless operations designed for urban areas, no steering wheel or pedals.
- Focus: Autonomous public transport and ride-sharing.
Zoox (by Amazon)
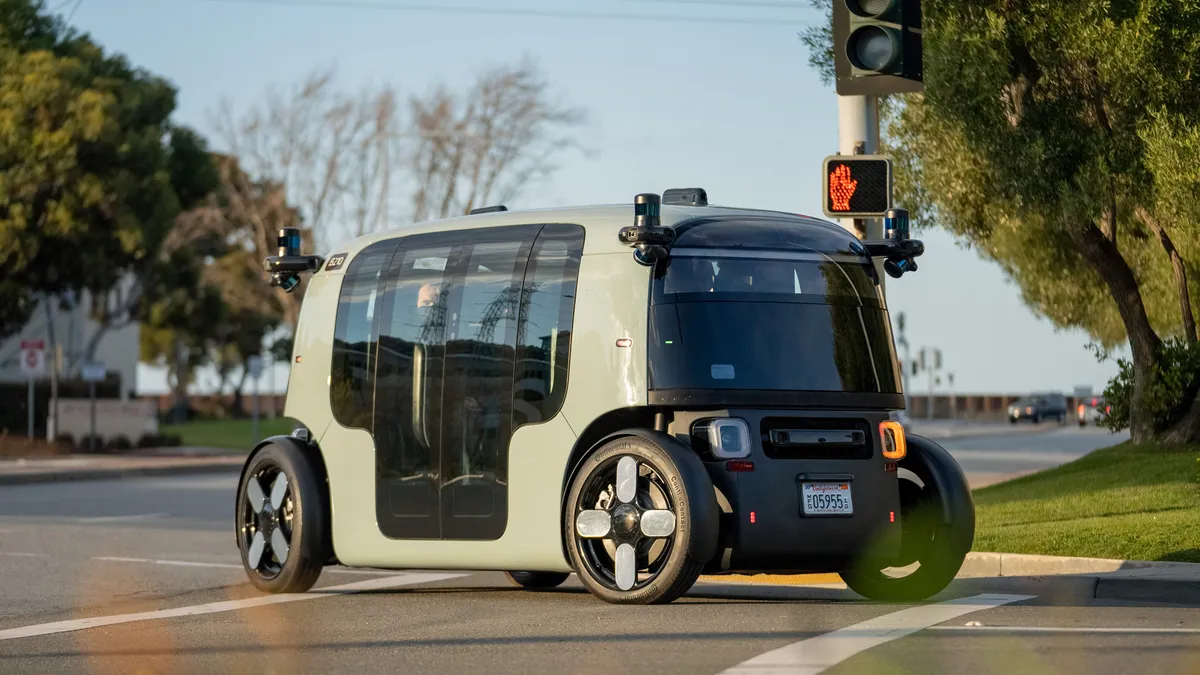

- A Level 4 autonomous vehicle.
- Features: Fully symmetrical design for bidirectional driving, designed for urban ride-sharing.
- Focus: Creating a futuristic, purpose-built autonomous vehicle for city transportation.
Audi Traffic Jam Pilot
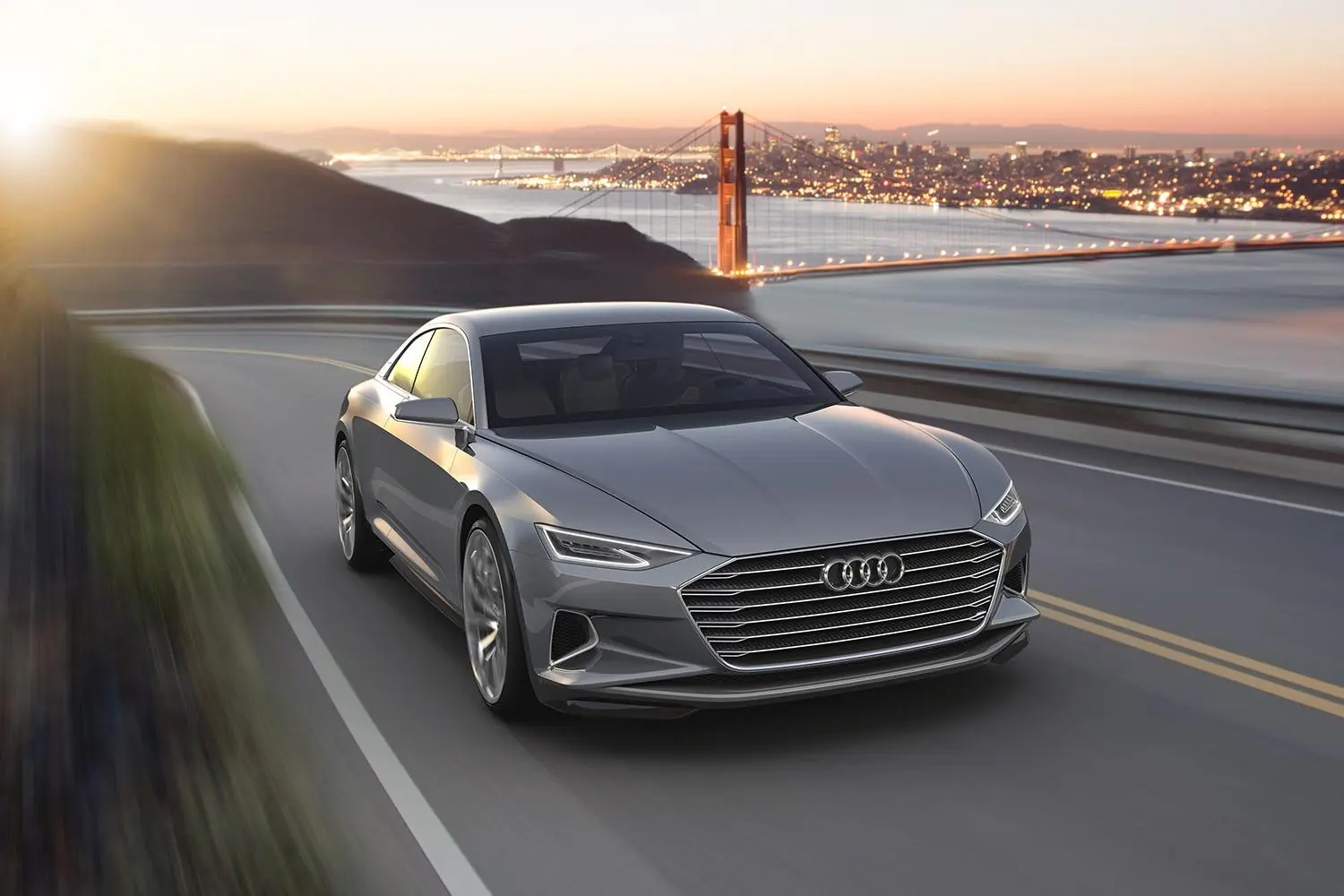

- A Level 3 autonomous system.
- Features: Hands-free driving in slow-moving traffic on highways, with the driver required to take control if conditions change.
- Focus: Enhancing urban driving comfort and reducing stress in traffic.
Comparison Table
| Feature/Model | Tesla Autopilot | Waymo One | Mercedes-Benz Drive Pilot | Cruise Origin | Zoox | Audi Traffic Jam Pilot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomy Level | Level 2 | Level 4 | Level 3 | Level 4 | Level 4 | Level 3 |
| Target Audience | Consumer vehicles | Ride-hailing users | Luxury car buyers | Urban commuters | Urban ride-sharers | Urban commuters |
| Notable Features | Adaptive cruise, lane-keeping | Fully driverless in zones | Highway hands-free driving | Driverless shuttle | Bidirectional driving | Traffic jam automation |
| Geographic Scope | Global (consumer cars) | Select cities (e.g., Phoenix) | Specific highways | Urban areas | Urban areas | Highways and cities |
| Unique Selling Point | Incremental autonomy | Fully driverless rides | Hands-free luxury driving | No steering/pedals | Futuristic design | Reducing traffic stress |
3. Connected Cars: The Internet of Things (IoT) on Wheels
What Are Connected Cars?
Connected cars are the cutting-edge result of integrating internet connectivity and advanced software into modern vehicles. These cars go beyond traditional driving by enabling seamless communication with other devices, networks, and services. As a crucial element of the Internet of Things (IoT), connected cars are transforming transportation into a smarter, safer, and more efficient experience. From navigation to entertainment and safety, these vehicles are redefining how we interact with our cars and the world around us.
Key Features
1. 5G Connectivity
5G connectivity is a game-changer for connected cars. With ultra-fast data transfer speeds and minimal latency, it enables real-time communication between vehicles, infrastructure, and cloud-based services. This ensures smoother navigation, instantaneous updates on traffic and road conditions, and a more immersive in-car experience through high-speed streaming and responsive infotainment systems.
2. Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X)
V2X communication is a cornerstone of connected car technology. This feature allows cars to interact with:
- Traffic Lights: Vehicles can receive updates about signal changes to optimize speed and fuel efficiency.
- Other Vehicles: Cars can share data about speed, location, and braking to avoid collisions and enable safer driving.
- Infrastructure: Roads, bridges, and parking systems can provide real-time updates about conditions, reducing congestion and accidents.
3. In-Car Infotainment
Connected cars offer advanced infotainment systems that deliver personalized content, music streaming, and seamless integration with smartphones. Drivers and passengers can access voice-activated navigation, entertainment apps, and even productivity tools while on the go.
4. Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
Gone are the days of visiting a dealership for software upgrades. Connected cars can receive OTA updates for their operating systems, ensuring that drivers always have access to the latest features, performance improvements, and security patches.
5. Predictive Maintenance
Connected vehicles monitor their systems continuously and use analytics to predict maintenance needs. For instance, the car can alert drivers about a failing component before it becomes a problem, reducing downtime and repair costs.
Examples and Comparisons
Connected cars have become a competitive space where automakers are integrating innovative features to appeal to different audiences. Let’s dive deeper into two popular models and how they compare:
BMW i7
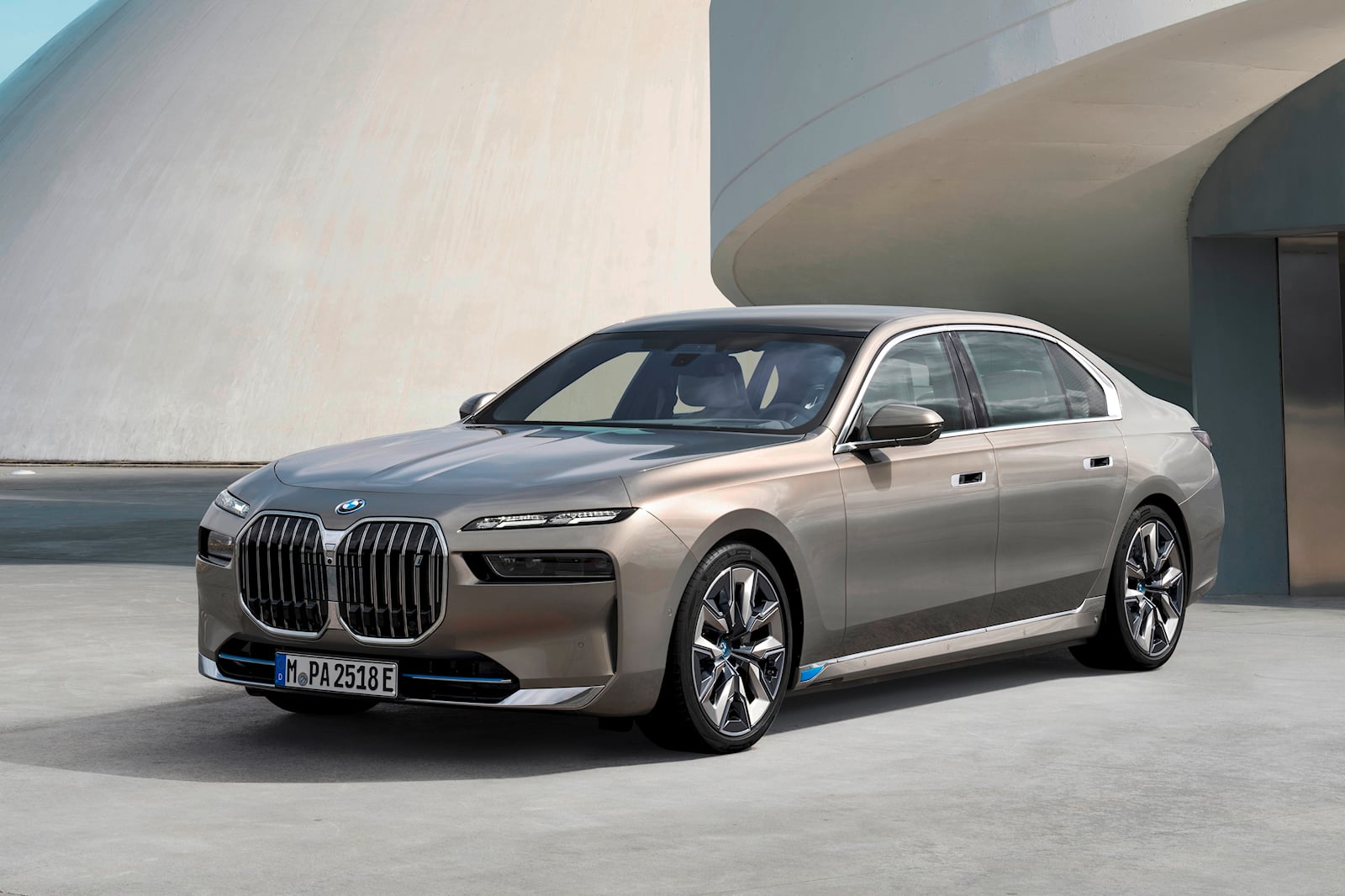

The BMW i7 stands as a pinnacle of luxury in the realm of connected cars. Designed for a premium driving experience, it offers a cutting-edge 31-inch rear-seat entertainment screen with 8K resolution, creating a theater-like experience for passengers. Its 5G connectivity ensures seamless streaming and access to cloud-based services. Additionally, the i7 integrates advanced navigation systems and AI-powered personal assistants, making it a tech-savvy luxury sedan.
Ford Mustang Mach-E
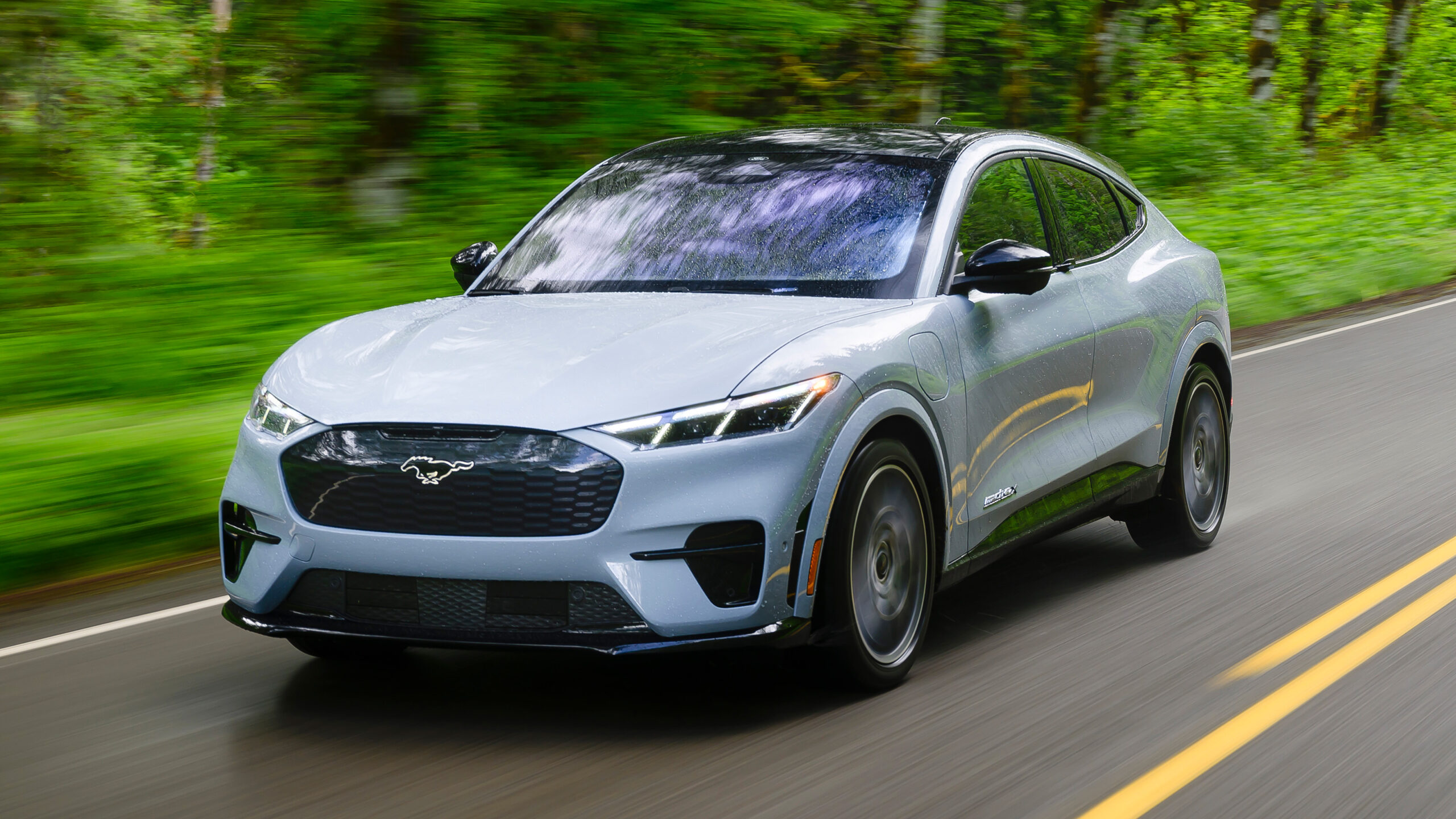

Ford’s Mustang Mach-E represents a more practical and versatile approach to connected car technology. It focuses on accessibility, offering over-the-air (OTA) updates to keep the car’s software up-to-date without requiring dealership visits. The Mach-E also boasts seamless smartphone integration, allowing users to control the vehicle through the Ford Pass app, which enables remote locking, starting, and monitoring.
Comparison
While both the BMW i7 and Ford Mustang Mach-E excel in connected technology, they cater to different market segments. BMW targets luxury and entertainment enthusiasts with cutting-edge screens and high-speed connectivity, whereas Ford prioritizes practicality and technological accessibility for everyday drivers.
Comparison Table: BMW i7 vs. Ford Mustang Mach-E
| Feature | BMW i7 | Ford Mustang Mach-E |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | Luxury segment seeking premium features and in-car entertainment | Practical users looking for affordable and advanced software functionality |
| Entertainment | 31-inch 8K rear-seat screen with theater-like experience | Basic infotainment with smartphone integration |
| Connectivity | 5G connectivity for seamless streaming and cloud services | Smartphone app integration via FordPass |
| Software Updates | Supports OTA updates for select features | Full OTA updates for system improvements |
| AI and Assistance | AI-powered personal assistants for navigation and in-car commands | Voice-controlled systems and app-based vehicle control |
| Unique Selling Point | Premium entertainment and connectivity for a luxury experience | Practical technology updates and remote monitoring at an affordable price |
4. Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): Enhancing SafetyWhat Is ADAS?
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) refer to a suite of technologies designed to assist drivers, enhance vehicle safety, and reduce the risk of accidents. These systems leverage a combination of sensors, cameras, radar, LiDAR, and artificial intelligence (AI) to monitor the vehicle’s surroundings in real-time. By analyzing data from these inputs, ADAS can provide warnings, automate certain driving tasks, and even take corrective actions to prevent collisions or mitigate their severity.
ADAS represents a critical step toward fully autonomous vehicles, bridging the gap between human-driven and self-driving cars. While these systems are not yet capable of replacing human drivers entirely, they significantly improve safety and convenience, making them a standard feature in modern vehicles.
Key Features of ADAS
1. Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)
- What It Does: ACC automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe following distance from the car ahead. Unlike traditional cruise control, which maintains a fixed speed, ACC uses radar or cameras to detect the speed of surrounding vehicles and adapts accordingly.
- How It Works: Sensors monitor the distance to the vehicle in front. If the car ahead slows down, ACC reduces speed; if the road clears, it accelerates back to the preset speed.
- Example: On a highway, ACC can make long drives less fatiguing by handling speed adjustments in traffic.
2. Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB)
- What It Does: AEB detects potential collisions and automatically applies the brakes if the driver fails to respond in time. This feature is particularly effective in preventing low-speed collisions, such as rear-end accidents.
- How It Works: Cameras and sensors continuously scan the road ahead. If an obstacle is detected and a collision is imminent, the system alerts the driver and, if necessary, applies the brakes.
- Example: In stop-and-go traffic, AEB can prevent accidents caused by sudden braking or distracted driving.
3. Lane-Keeping Assist (LKA)
- What It Does: LKA helps prevent unintentional lane departures by gently steering the vehicle back into its lane if it begins to drift.
- How It Works: Cameras detect lane markings and monitor the vehicle’s position. If the car starts to drift without a turn signal, the system provides steering input to correct its path.
- Example: On long highway drives, LKA can reduce driver fatigue and prevent accidents caused by drowsiness or distraction.
4. Blind Spot Detection (BSD)
- What It Does: BSD alerts the driver to vehicles in their blind spots, reducing the risk of collisions during lane changes.
- How It Works: Sensors mounted on the sides of the vehicle monitor adjacent lanes. If a vehicle is detected in the blind spot, a warning light appears on the side mirror or dashboard.
- Example: When changing lanes on a busy highway, BSD provides an extra layer of safety by warning the driver of unseen vehicles.
5. Traffic Sign Recognition (TSR)
- What It Does: TSR identifies and displays traffic signs, such as speed limits and stop signs, on the vehicle’s dashboard or heads-up display.
- How It Works: Cameras capture images of road signs, and AI algorithms interpret and display the information to the driver.
- Example: In unfamiliar areas, TSR helps drivers stay aware of speed limits and other road regulations.
6. Parking Assistance
What It Does: Parking assistance systems use cameras and sensors to help drivers park more easily and accurately. Some advanced systems can even park the car autonomously.
How It Works: Sensors detect obstacles and provide visual or auditory cues to guide the driver. In fully automated systems, the car takes control of steering, acceleration, and braking.
Example: Parallel parking in tight urban spaces becomes stress-free with parking assistance.
Examples of ADAS in Popular Cars
Toyota Corolla
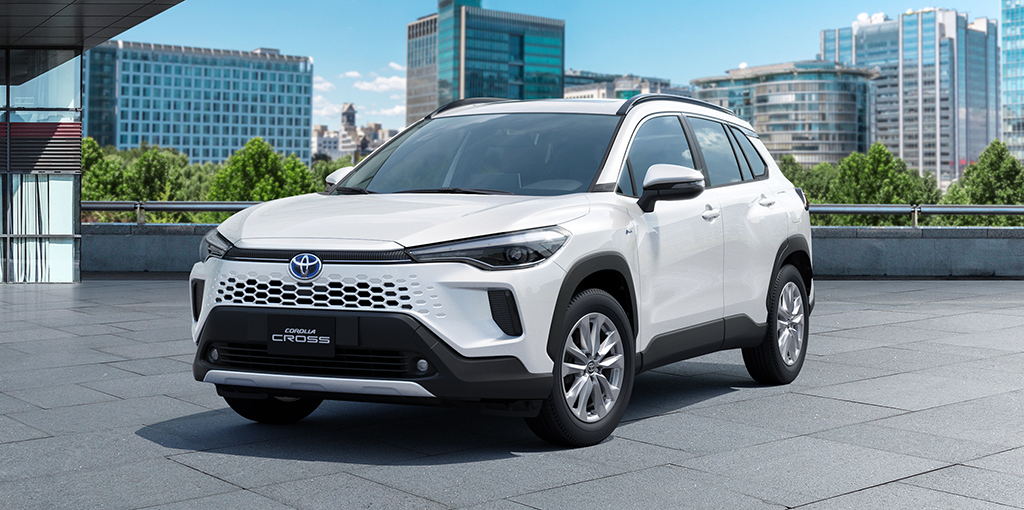

Offers standard ADAS features like adaptive cruise control, lane departure alert, and automatic high beams.
Tesla Model 3

Features Autopilot, which includes adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and automatic emergency braking.
Volvo XC90

Known for its comprehensive safety suite, including blind spot detection, lane-keeping assist, and pilot assist.
Comparison Table: Examples of ADAS in Popular Cars
| Feature | Tesla Model 3 | Volvo XC90 | Toyota Corolla |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADAS System Name | Autopilot | Pilot Assist | Toyota Safety Sense |
| Adaptive Cruise Control | Yes, advanced with traffic-aware capabilities | Yes, integrated with Pilot Assist | Yes, included as standard |
| Lane-Keeping Assist | Yes, helps maintain the car’s position in the lane | Yes, active steering for lane centering | Yes, alerts and corrective steering |
| Automatic Emergency Braking | Yes, detects vehicles and pedestrians | Yes, detects vehicles, cyclists, and large animals | Yes, detects vehicles and pedestrians |
| Blind Spot Detection | Not included by default but available in higher trims | Yes, warns about vehicles in adjacent lanes | Yes, included in higher trims |
| Automatic High Beams | Not included | Yes, adaptive high beams | Yes, adjusts headlights for optimal visibility |
| Unique Selling Point | Advanced driver-assistance features with over-the-air updates | Renowned for comprehensive safety and additional large-animal detection | Standard ADAS features included even in the base model, making it highly accessible |
| Target Audience | Tech-savvy drivers seeking semi-autonomous driving features | Drivers prioritizing safety and comfort in a premium SUV | Budget-conscious drivers who value safety without compromising on essential ADAS features |
5. Sustainability and Green Technology
What Is Green Technology in Automotive?
Green technology in the automotive industry represents a commitment to reducing the environmental impact of vehicles and promoting sustainable practices. This encompasses the development of alternative fuels, energy-efficient vehicle designs, and eco-friendly manufacturing processes. The goal is to create transportation solutions that minimize carbon footprints while maintaining performance and convenience. As the world shifts towards addressing climate change and reducing dependency on fossil fuels, green technology is becoming a critical focus for automakers and policymakers alike.
Key Innovations in Green Automotive Technology
- Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Hydrogen fuel cells are a groundbreaking innovation in green technology. They generate electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, producing only water vapor as a byproduct. These systems are highly efficient, quiet, and emit zero harmful pollutants. - Solar-Powered Cars
Solar-powered cars use photovoltaic panels to harness energy from the sun, which supplements battery power or directly drives the vehicle. While full solar-powered cars are still in the experimental stage, models like the Lightyear 0 demonstrate how solar panels can increase driving range and reduce reliance on charging stations. - Alternative Fuels
Beyond hydrogen and electricity, alternative fuels like biofuels and synthetic fuels are being explored. Biofuels, derived from organic materials like algae and crops, offer a renewable energy source. - Energy-Efficient Vehicle Designs
Aerodynamics and lightweight materials are critical to improving vehicle efficiency. Cars designed with advanced materials like carbon fiber and aluminum reduce energy consumption by requiring less power to move. - Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Automakers are adopting greener methods in manufacturing, including the use of recycled materials, renewable energy in factories, and carbon-neutral production processes. For example, BMW’s iFactory focuses on sustainability by integrating renewable energy sources and reducing water usage. - Hybrid Technologies
Hybrid vehicles combine traditional internal combustion engines with electric powertrains, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Plug-in hybrids take this a step further by allowing short-range driving purely on electric power. - Recyclable Batteries
With the rise of electric vehicles, battery recycling has become a significant focus. Innovations in battery recycling technologies ensure that valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel can be reused, reducing environmental harm and production costs.
Examples and Comparisons in Green Technology
Here’s a look at some leading vehicles showcasing green technology and how they compare:
Toyota Mirai
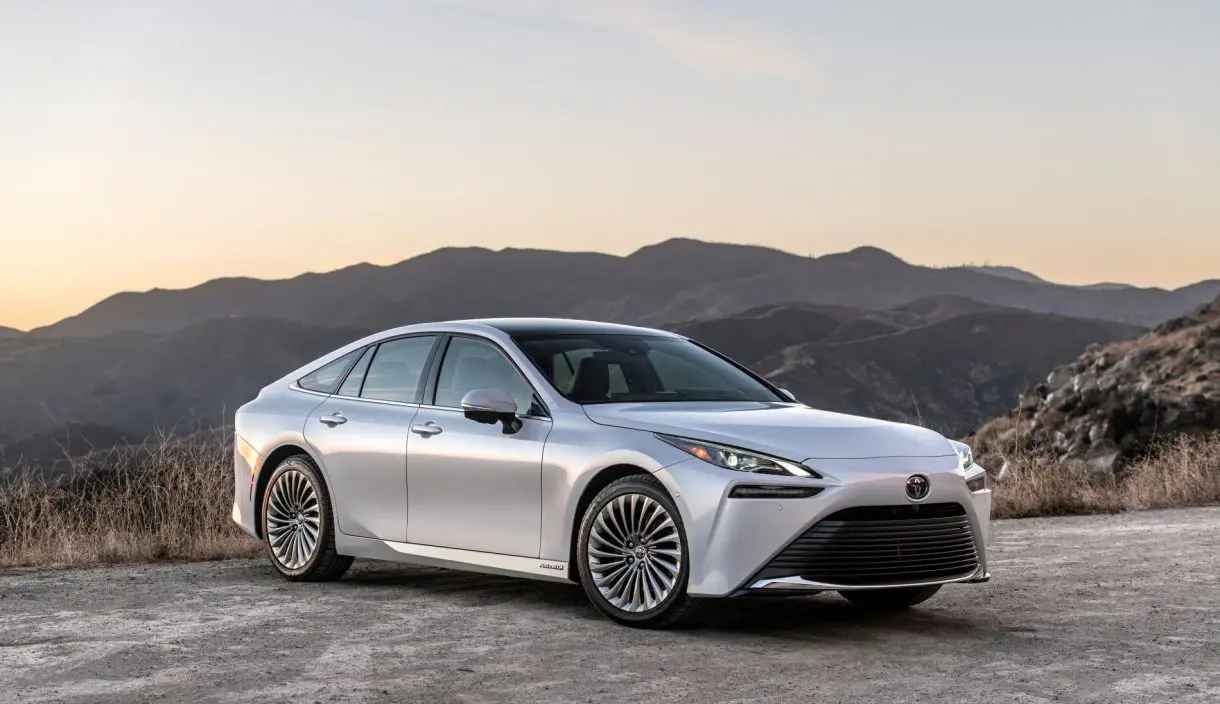

The Toyota Mirai is a pioneer in hydrogen fuel cell technology. It emits only water vapor and offers a range of approximately 402 miles on a full tank of hydrogen. It highlights the potential of hydrogen as a clean fuel, though refueling infrastructure remains a challenge.
Lightyear 0
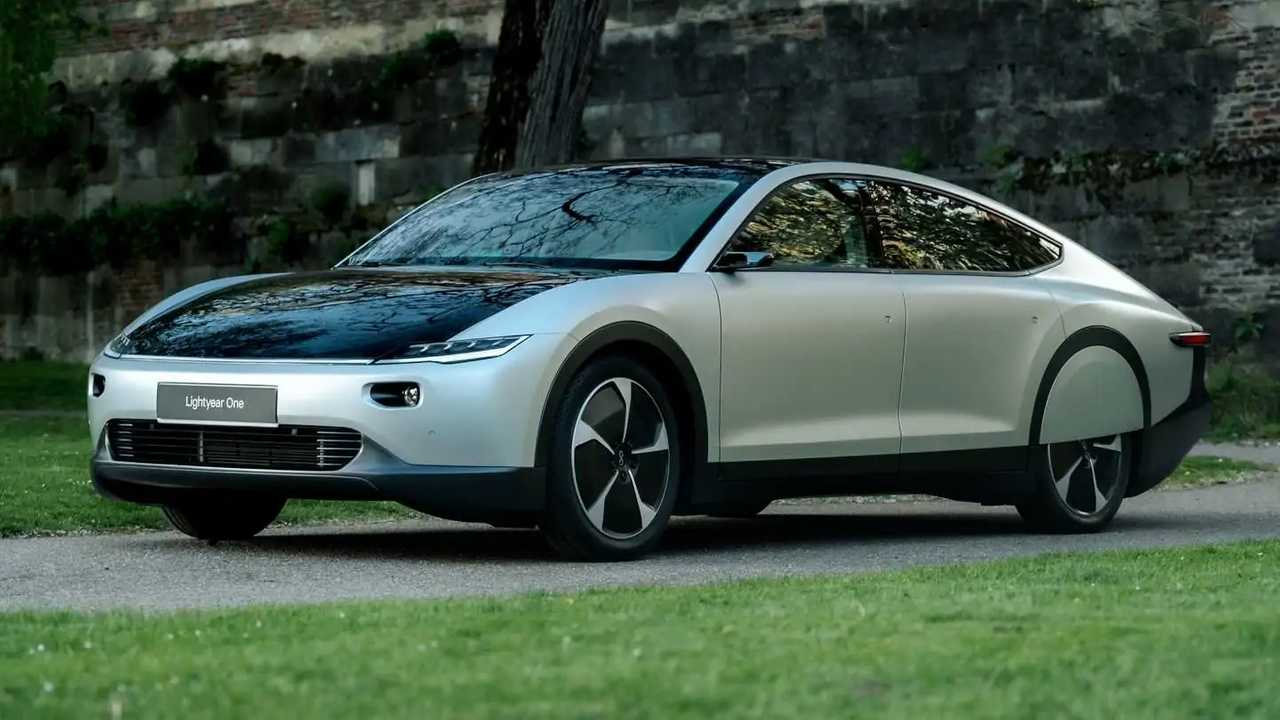

The Lightyear 0 integrates solar panels into its design, enabling it to charge directly from sunlight. This model can supplement its battery with solar energy, adding up to 40 miles of range per day in sunny conditions. It’s ideal for regions with ample sunlight, though its high price point limits accessibility.
Tesla Model 3

Tesla’s electric vehicles, like the Model 3, exemplify advancements in energy-efficient designs and battery technology. The Model 3 offers long-range electric driving with zero tailpipe emissions, supported by Tesla’s extensive Supercharger network. It does not rely on alternative fuels like hydrogen or solar but is a benchmark for EV efficiency and affordability.
Hyundai NEXO
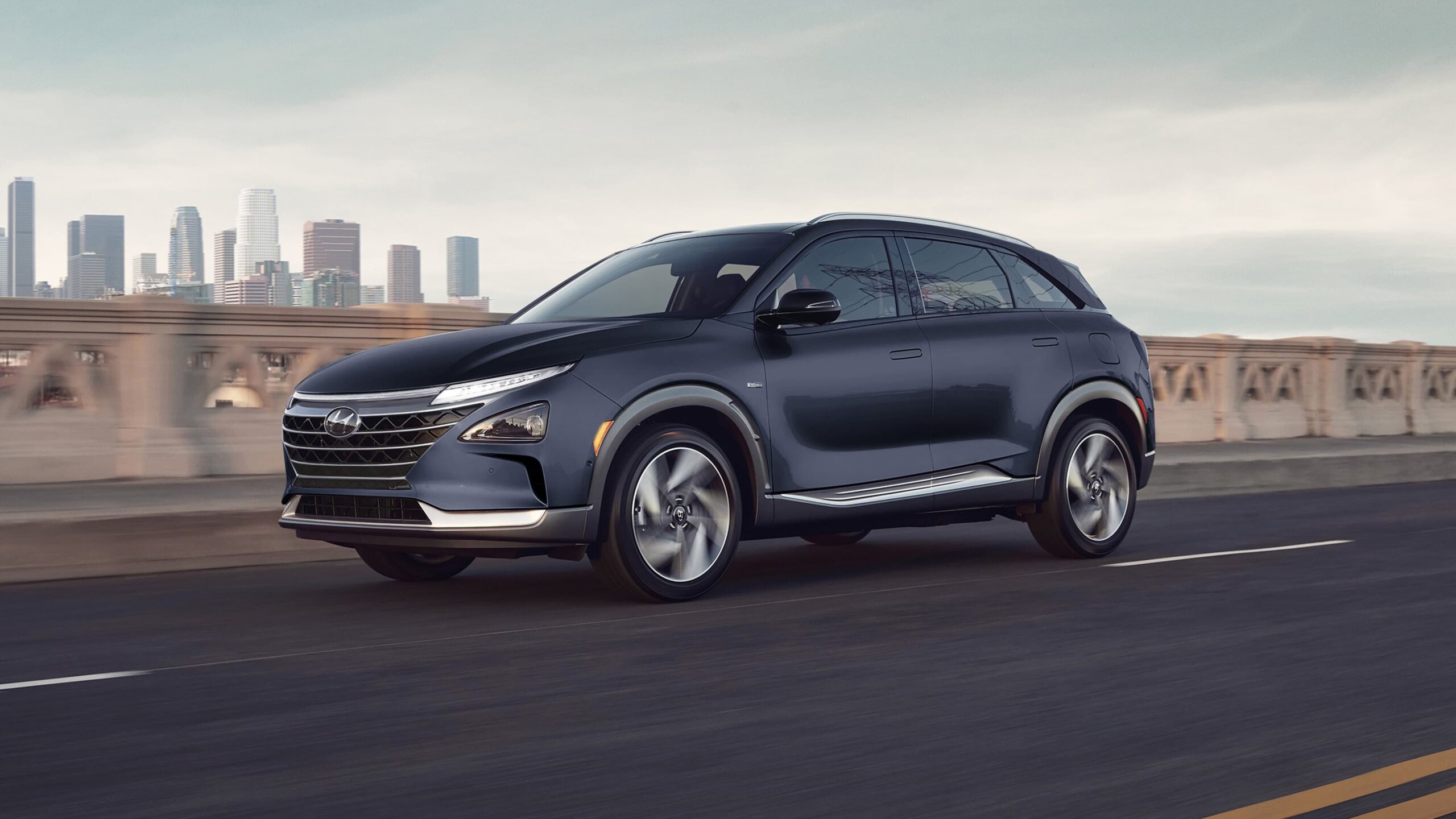

The Hyundai NEXO is another hydrogen-powered vehicle, offering a range of up to 380 miles. It focuses on sustainability, featuring eco-friendly interior materials and advanced safety features. The NEXO competes closely with the Toyota Mirai in the hydrogen fuel cell market.
Comparison Table: Green Technology in Leading Vehicles
| Vehicle | Technology | Range (miles) | Emission | Unique Feature | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toyota Mirai | Hydrogen Fuel Cell | 402 | Water vapor | Zero tailpipe emissions; efficient hydrogen use | Limited refueling infrastructure |
| Lightyear 0 | Solar Power + Battery | 388 (+40/day solar) | Zero emissions | Solar panels for direct sunlight charging | High price, niche application |
| Tesla Model 3 | Fully Electric (Battery-Powered) | 358 | Zero emissions | Extensive Supercharger network; affordable EV | Relies on charging infrastructure |
| Hyundai NEXO | Hydrogen Fuel Cell | 380 | Water vapor | Eco-friendly interior; safety focus | Limited refueling infrastructure |
6. Futuristic Concepts: Beyond the Road
What Are Futuristic Automotive Concepts?
Futuristic automotive concepts are groundbreaking ideas and prototypes that redefine the way we think about transportation. These innovations aim to address challenges like urban congestion, long-distance travel, and enhanced driver experiences while pushing the boundaries of traditional vehicle design and functionality. From flying cars to hyperloop systems and augmented reality (AR) windshields, these concepts are shaping the future of mobility.
Key Examples
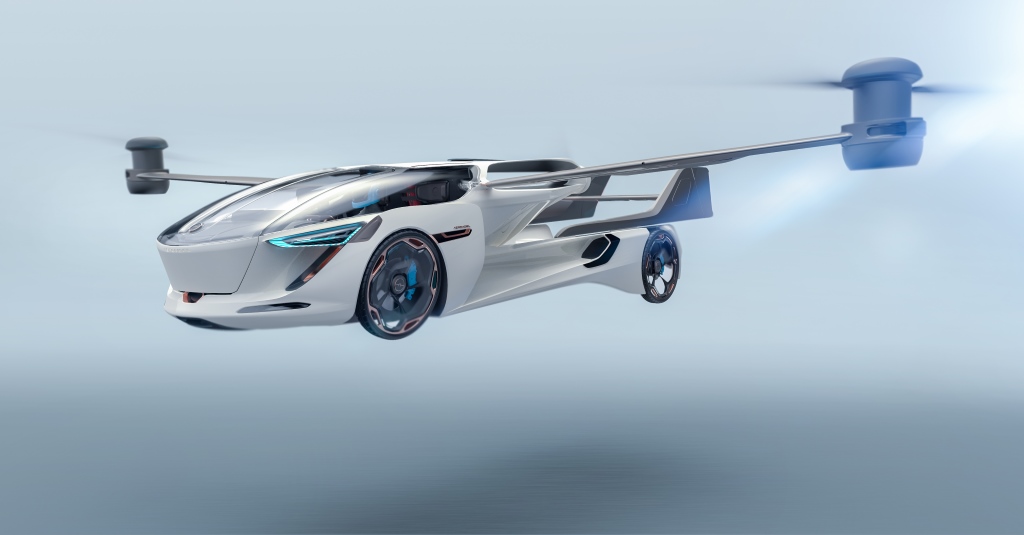
Flying Cars
Flying cars, also known as eVTOL (electric vertical takeoff and landing) vehicles, represent a major leap in personal urban air mobility. These vehicles combine the functionality of a car with the capabilities of an aircraft, offering solutions for traffic congestion in densely populated areas.
- Example: AeroMobil 5.0, which can transform from a road vehicle to an aircraft in minutes.

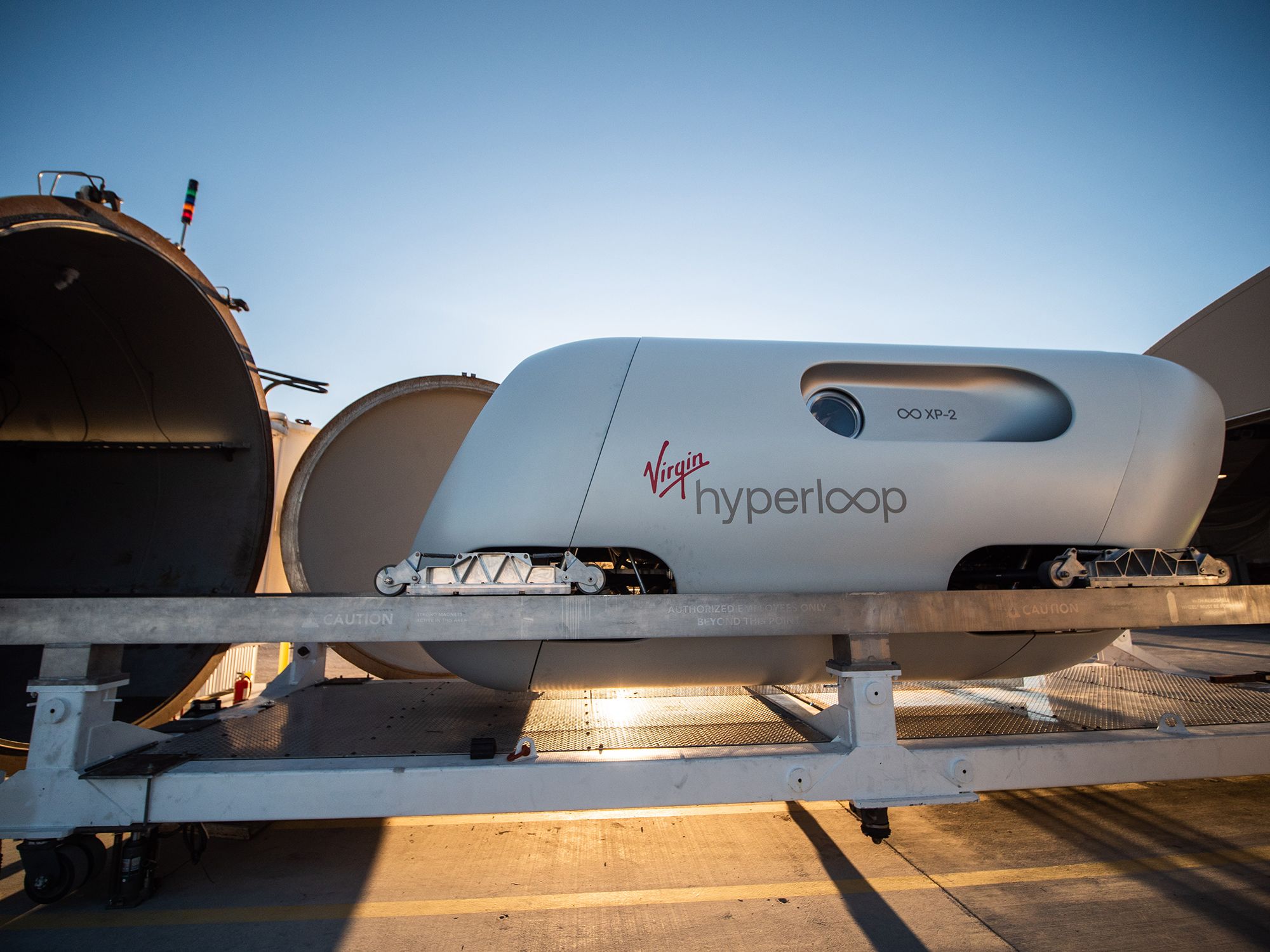
Hyperloop Systems
Hyperloop systems are high-speed transportation concepts where pods travel through low-pressure tubes at incredible speeds, reducing travel time for long distances.
- Example: Virgin Hyperloop, which has been developing prototypes with speeds up to 670 mph.

Augmented Reality (AR) Windshields
AR windshields overlay critical driving information, such as navigation routes, traffic updates, and hazard alerts, directly onto the driver’s view.
- Example: Companies like WayRay are integrating AR into vehicle designs for an immersive and safer driving experience.
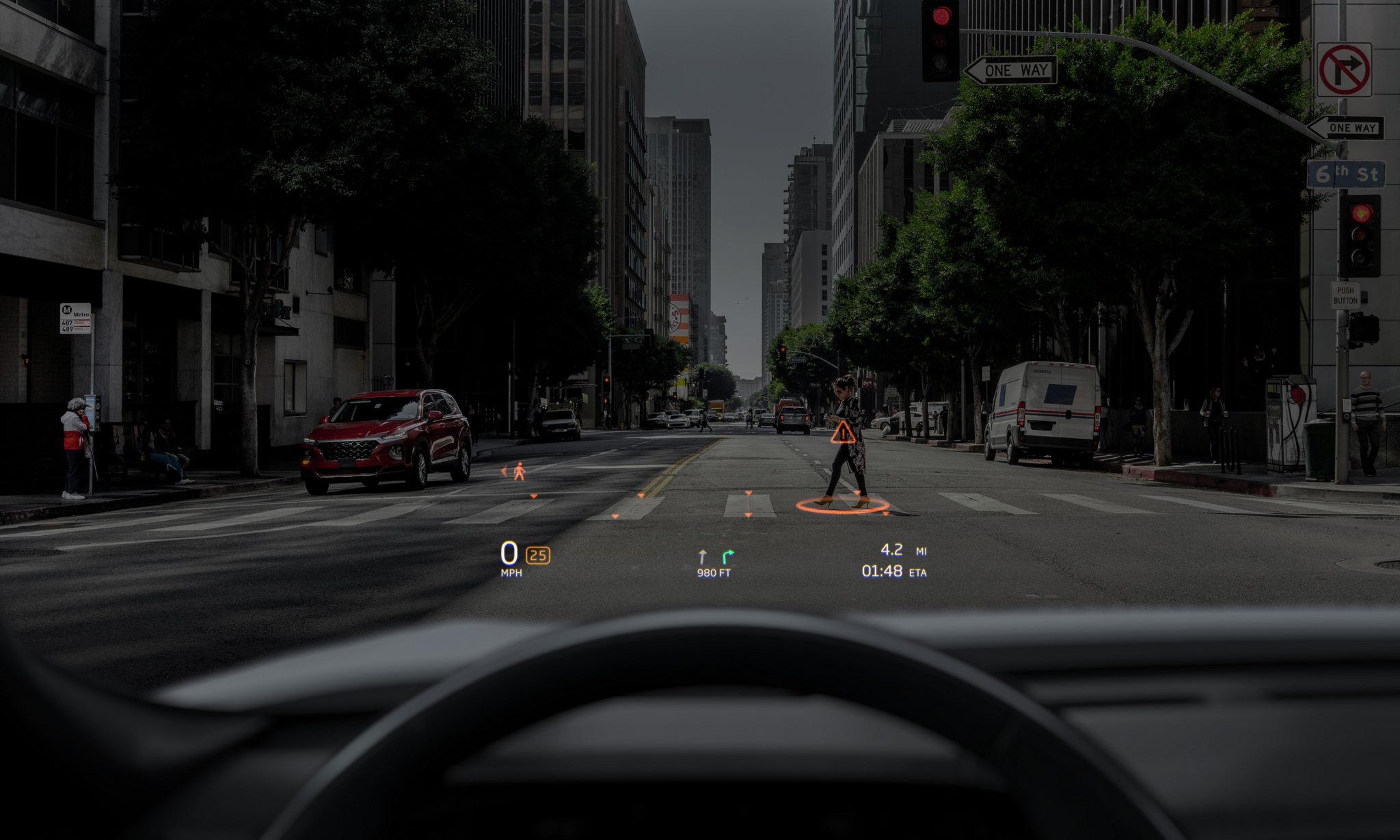
Groundbreaking Performance in EVs
Futuristic EVs focus on record-breaking performance and long-range capabilities.
- Example: Tesla Roadster (2025), which promises a 0-60 mph time of 1.9 seconds and a range of 620 miles, positioning it as a high-performance vehicle for the future.

Comparison Table: Futuristic Automotive Concepts
| Concept | Example | Unique Feature | Primary Use Case | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flying Cars | AeroMobil 5.0 | Transforms from road vehicle to aircraft | Urban air mobility | High cost, regulatory challenges |
| Hyperloop Systems | Virgin Hyperloop | High-speed pods in low-pressure tubes | Long-distance travel | Expensive infrastructure, untested scalability |
| Augmented Reality (AR) | WayRay AR Windshields | Navigation, hazard alerts on the windshield | Enhanced safety and user experience | High development cost, driver adaptation |
| High-Performance EVs | Tesla Roadster (2025) | 0-60 mph in 1.9 seconds, 620-mile range | Ground-breaking EV performance | Expensive and limited to high-end market |
7. Challenges and Ethical Considerations
What Are the Challenges?
- Data Privacy: Connected cars collect vast amounts of data, raising concerns about user privacy.
- Cybersecurity: Hackers could potentially take control of autonomous or connected vehicles.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Self-driving cars must make split-second decisions in life-threatening situations.
Examples
- Tesla’s Data Collection: Criticized for collecting and storing user data without explicit consent.
- Cybersecurity Breaches: Instances of hackers remotely controlling Jeep Cherokees.
Conclusion
The future of automotive technology is undeniably exciting, promising to redefine how we think about and interact with vehicles. Innovations such as electric vehicles (EVs), autonomous driving, connected cars, and green technology are paving the way for smarter, safer, and more sustainable transportation. These advancements are not just enhancing convenience and performance but are also addressing critical global challenges like climate change, urban congestion, and energy efficiency.
However, as we embrace these transformative technologies, it’s crucial to navigate the accompanying challenges. Issues like data privacy, cybersecurity risks, and ethical dilemmas in autonomous decision-making must be tackled with care and foresight. Collaboration among automakers, governments, and technology companies will play a pivotal role in shaping policies, setting safety standards, and building public trust in these emerging innovations.
At the same time, futuristic concepts like flying cars, hyperloop systems, and augmented reality (AR) windshields offer a glimpse into the possibilities that lie beyond the road. While these ideas may seem like science fiction today, they underscore the boundless potential of human ingenuity and the role of technology in driving the cars of tomorrow.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, staying informed about these trends is essential for consumers, businesses, and enthusiasts alike. At Tech on Wheels, we are committed to providing you with comprehensive insights and in-depth analysis of the latest developments in automotive technology. From detailed comparisons of groundbreaking models to updates on emerging technologies, we aim to keep you at the forefront of this exciting journey.
The road ahead is full of innovation and discovery. Join us as we explore the transformative power of technology in reshaping the automotive landscape and beyond. Stay tuned for more articles, insights, and updates on the innovations driving the future of mobility!


