Your cart is currently empty!

What Is the Internet of Things (IoT)?: A Beginner’s Introduction to Connected Devices
Discover the Internet of Things (IoT) in this beginner-friendly guide. Learn how connected devices like smart home gadgets and industrial sensors are transforming daily life and business operations.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly transforming the way we live, work, and interact with the world. From smart thermostats to connected cars, IoT is reshaping industries and enhancing daily life. This article will explore what IoT is, how it works, its applications, and why it matters, providing a comprehensive guide for beginners.
Understanding the Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data over the internet. These devices, often embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies, collect and share information to perform specific tasks or improve efficiency.
For example, a smart refrigerator can monitor its contents and notify you when you’re running low on milk. Similarly, smart city solutions like connected traffic lights can optimize traffic flow to reduce congestion.
Key Components of IoT
To understand IoT better, let’s break down its essential components:
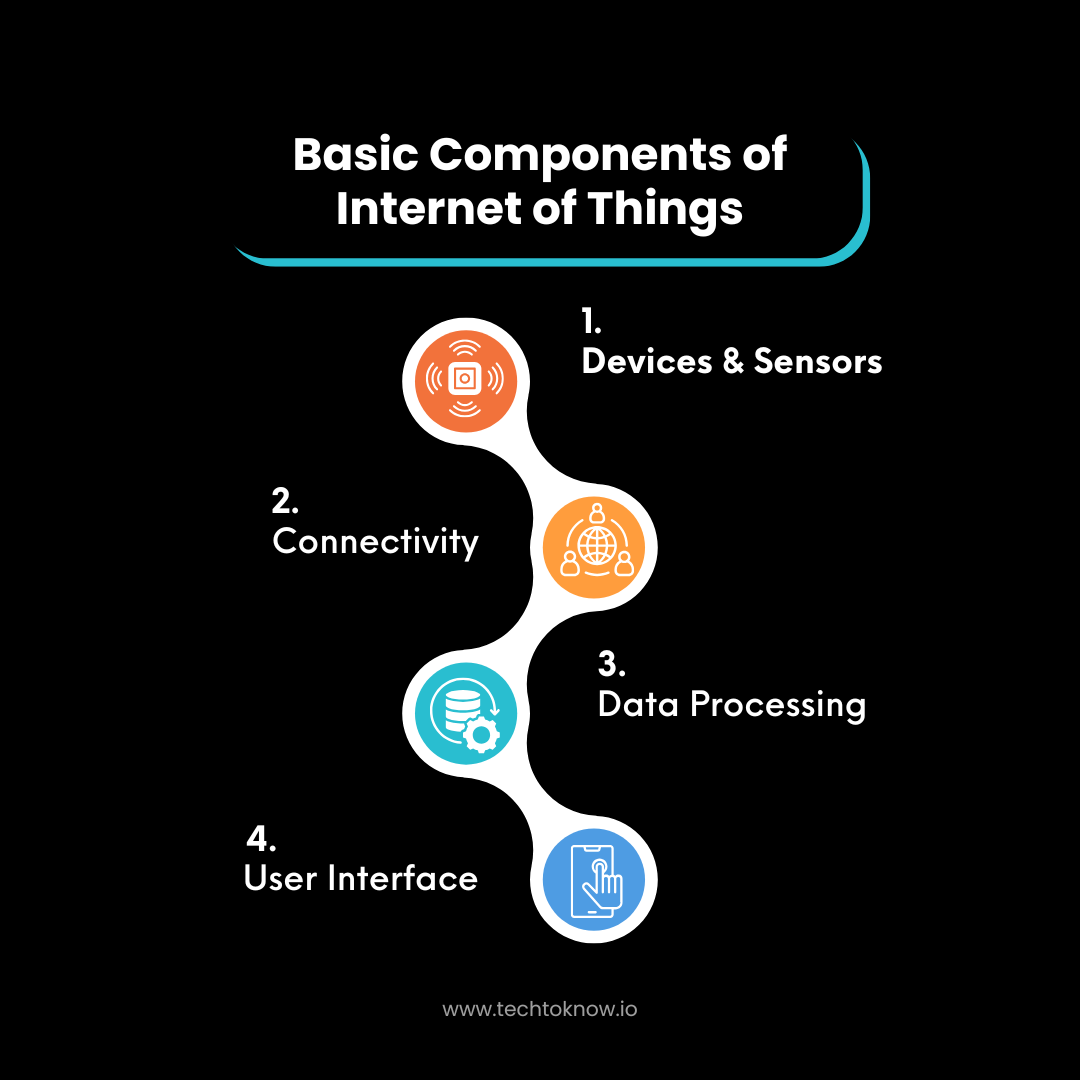
- Devices and Sensors
- These are the physical objects that collect data from their surroundings. Examples include temperature sensors, GPS trackers, and motion detectors.
- Connectivity
- IoT devices connect to the internet using various protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks. This connectivity enables data transfer.
- Data Processing
- Once data is collected, it is processed either locally (on the device) or remotely (in the cloud).
- User Interface
- The data collected by IoT devices is presented to users through apps or dashboards, allowing them to monitor or control the devices.
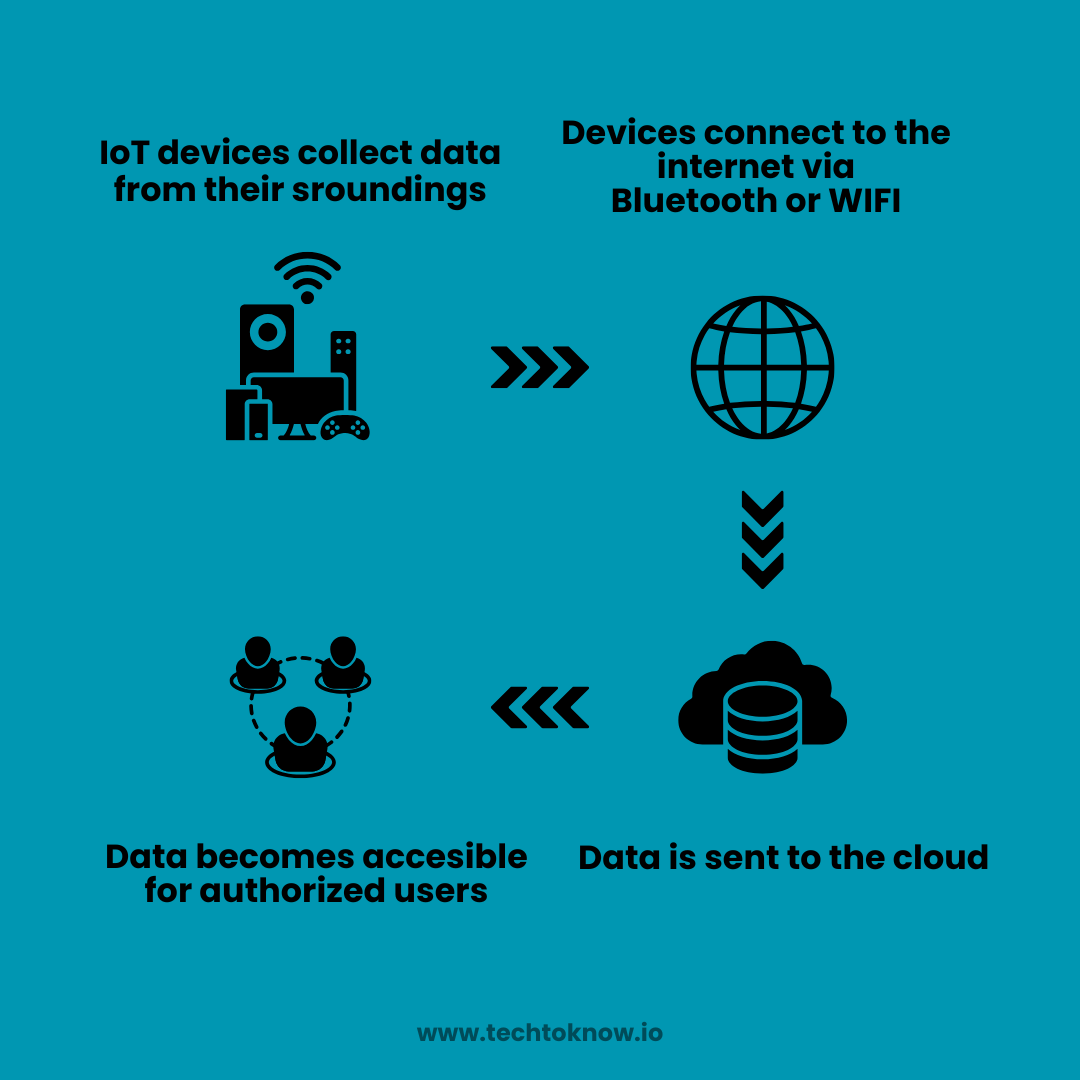
Diagram: How IoT Works
The diagram illustrates the typical Internet of Things ecosystem, showing how devices connect, collect data, process it, and deliver insights to users.
Applications of IoT
There is a wide range of applications of IoT(Internet of Things) across various industries. Here are some of the most notable ones:
- Smart Homes
- Devices like Amazon Echo, Google Nest, and smart bulbs automate household tasks. For instance, you can control lighting, temperature, and security systems using your smartphone.
- Healthcare
- Wearable devices like Fitbit or Apple Watch monitor vital signs such as heart rate and activity levels, providing valuable health insights.
- Agriculture
- Smart sensors monitor soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health, optimizing farming practices and boosting yields.
- Transportation
- IoT-enabled vehicles use GPS and sensors for navigation and real-time traffic updates. Autonomous cars like Tesla rely heavily on IoT technologies.
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
- Manufacturing plants use connected devices to monitor equipment performance, predict maintenance needs, and improve productivity.
Benefits of IoT
- Enhanced Efficiency
- Automates routine tasks, saving time and resources.
- Cost Savings
- Reduces energy consumption and operational expenses. For example, smart meters optimize electricity usage.
- Improved Decision-Making
- Provides real-time data for informed decisions, such as adjusting production schedules based on equipment performance.
- Convenience
- Enables remote monitoring and control of devices, enhancing user experience.
IoT offers numerous advantages, including:
Challenges of IoT
Despite its advantages, IoT also poses several challenges:
- Security Risks
- Connected devices are vulnerable to hacking, making cybersecurity a top priority.
- Privacy Concerns
- IoT devices collect vast amounts of data, raising concerns about how this information is used and stored.
- Interoperability Issues
- Different devices and platforms may not communicate seamlessly, limiting functionality.
- High Implementation Costs
- Initial setup and maintenance can be expensive for businesses and individuals.
IoT Devices and Their Uses
| Device Type | Example | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Thermostat | Nest Thermostat | Energy-efficient home heating/cooling |
| Fitness Tracker | Fitbit | Health monitoring |
| Smart Doorbell | Ring Doorbell | Home security |
| Connected Cars | Tesla Model 3 | Autonomous driving |
| Industrial Sensors | Siemens Sensors | Equipment monitoring in factories |
Pro Tip
When setting up IoT devices, always update their firmware and use strong passwords to enhance security. Consider investing in a reliable router with built-in IoT security features.
The Future of IoT
The IoT industry is expected to grow exponentially, with billions of devices coming online in the next decade. Innovations like 5G connectivity, 2nm chips, edge computing, and AI integration will drive this growth. These advancements promise faster data processing, reduced latency, and more intelligent decision-making capabilities.
The Internet of Things is an exciting and transformative technology. By understanding its basics, applications, and challenges, you can leverage IoT to enhance your personal and professional life. Whether it’s automating your home or optimizing industrial processes, IoT holds endless possibilities for innovation.
FAQ
What is the main purpose of IoT?
The primary goal of IoT is to connect devices, enabling them to communicate and share data for improved efficiency, convenience, and decision-making.
Is IoT only for businesses?
No, IoT benefits individuals through smart home devices, wearables, and connected appliances, in addition to business applications.
What are the risks of IoT?
Security and privacy risks are the main concerns, as IoT devices can be hacked or misused if not properly secured.
How can I start using IoT at home?
Begin with simple devices like smart bulbs, thermostats, or voice assistants, and gradually expand your ecosystem.
What is the role of 5G in IoT?
5G technology enhances IoT by providing faster connectivity, lower latency, and the ability to support more devices simultaneously.
How can I secure my IoT devices effectively?
Use strong, unique passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and ensure devices receive regular software updates. Discover more strategies in our article on cybersecurity best practices.


